Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Fujimori, Hiroshi*
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(6), p.062802_1 - 062802_24, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:36.4(Physics, Nuclear)As hadron accelerators for such as the ADS and spallation neutron source achieve increasing beam power, damage to targets is becoming increasingly severe. To mitigate this damage, nonlinear beam optics based on octupole magnets is attractive. Nonlinear optics can decrease the beam-focusing hazard due to failure of the rastering magnet. As a side effect of nonlinear optics, the beam size is known to expand drastically compared with linear optics. Nonlinear effects have been studied via a simplified filament model that ignores beam-divergence spread at the octupole magnet. In this study, a new generalized model is proposed for application to an octupole magnet, regardless of the filament-model approximation. It is found that the transverse distribution obtained by beam tracking can be specified by the introduction of only two parameters, namely the normalized octupole strength of 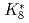 and the
and the 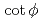 of the phase advance. To achieve the two antagonistic requirements of reduction of the beam-peak density and minimization of the beam loss, the transverse distribution is surveyed for a large range of beam position. It is found that a bell-shaped distribution with
of the phase advance. To achieve the two antagonistic requirements of reduction of the beam-peak density and minimization of the beam loss, the transverse distribution is surveyed for a large range of beam position. It is found that a bell-shaped distribution with 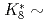 1 and
1 and 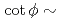 3 can satisfy requirements. This result is applied to beam transport in the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. The calculation result given by the present model shows good agreement with the experimental data, and the peak current density is reduced by 50% compared with the linear-optics case.
3 can satisfy requirements. This result is applied to beam transport in the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. The calculation result given by the present model shows good agreement with the experimental data, and the peak current density is reduced by 50% compared with the linear-optics case.
Yamamoto, Kazami
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.333 - 337, 2019/07
J-PARC 3GeV Synchrotron (RCS) started beam commissioning in 2007. The beam commissioning has been continued to increase the beam power for users. In a high-intensity hadron accelerator such as J-PARC, it is essentially important to reduce the activation due to beam loss and to suppress the exposure of workers. For this purpose, RCS has continued to study and countermeasure for the causes of beam loss from the initial stage of beam commissioning. At present, stable user operation is continuing at 500 kW. This value is half the design beam power of 1 MW, and the residual doses are being maintained enough small so that the maintenance work does not be hindered. In this report, we will introduce the history and measures of the residual doses in RCS so far, and the situation of the exposure dose of workers during maintenance work.
Hayashi, Naoki; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1096 - 1100, 2019/07
It is necessary to understand the reason why the accelerator has been interrupted due to beam loss or other machine mal function in order to keep high availability in long term period. At J-PARC RCS, 25 Hz rapid-cycling synchrotron, there is a system to record beam intensity and beam loss monitor signal for all pulses with 10 ms period. At this time, in addition, new system to archive data with better time resolution if interlocked events occurred has been introduced. Using these archived data, the events only RCS BLM gives MPS have been analyzed and it turns out that these events are related to the ion source discharge which makes very low intensity within less than a second. In this paper other typical events are presented and discuss how to improve the accelerator performance in future.
Hayashi, Naoki; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Miura, Akihiko; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*
Proceedings of 7th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2018) (Internet), p.219 - 223, 2019/01
J-PARC is a multi-purpose facility. Accelerator stability is the one of important issues for users of this facility. To realize stable operation, we must collect data on interlocked events and analyze these data to determine the reasons for the occurrence of such events. In J-PARC Linac, data of interlocked events have been recorded using several some beam loss monitors and current monitors, and these data have been are analyzed and classified. In J-PARC RCS, new instrumentation is being introduced to obtain beam position. We discuss the present status and future plans related to this subject.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Kato, Shinichi; Okabe, Kota; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.1048 - 1050, 2018/06
The charge exchange multi-turn beam injection scheme is adopted in the J-PARC 3GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron Accelerator (RCS) due to achieve 1MW beam power operation. In the conventional multi-turn beam injection scheme, which is provided by only the septum and bump magnets, injecting turn numbers are limited by the beam losses at the septum. On the other hand, charge exchange multi-turn beam injection does not cause the beam losses at the septum; there is no restriction in principle on the injecting turn number. However, high residual doses are observed around the stripper foil. During the charge exchange multi-turn beam injection, not only the injecting beam but also circulating beam hit the foil, and then a large number of secondary particles, namely protons and neutrons, are generated. PHITS simulation results indicate that the secondary particles cause the high residual doses around the foil. To verify this examination, secondary particles measurement is key issue. Then, a new independent type foil introducing device is installed in the 100-deg dump beam transport line in order to construct a simple experimental system for secondary particle measurements. We plan the two experiments by using this system; one is a directly secondary particle detecting method, and the other is a radioactivation analysis method with metal sample pieces. Now, we started the study of how the identification of species and energies of the secondary particles with PHITS code. Irradiation target of Cu is adopted and irradiated proton or neutron beam with various energy range. Then radio-nuclides emitted the  -ray are picked up. Moreover, the radio-nuclides, whose reaction efficiencies due to beam species or energy are different, are searched for the indicator of the secondary particles. From the simulation results,
-ray are picked up. Moreover, the radio-nuclides, whose reaction efficiencies due to beam species or energy are different, are searched for the indicator of the secondary particles. From the simulation results,  Zn is extremely suitable for a proton beam indicator, and
Zn is extremely suitable for a proton beam indicator, and  Co and
Co and  Co are also suited for a neutron and proton indicator respectively.
Co are also suited for a neutron and proton indicator respectively.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kato, Shinichi; Kinsho, Michikazu; Okabe, Kota
Proceedings of 6th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2017) (Internet), p.461 - 465, 2018/03
In the J-PARC RCS, a large fraction of our effort has been concentrated on reducing and managing beam losses to achieve 1MW high power proton beam operation. Standard beam loss monitor (BLM), which is installed outside of the magnet in every cell of beam optics and detect the beam loss at wide area in each cell, is insufficient to investigate finer beam loss mechanism in the ring. Thus we developed new scintillation type BLM to detect the beam loss at spot area on the vacuum chamber inside the magnet. The new BLM has separating structure a photomultiplier (PMT) from a plastic scintillator and connecting with optical fibres. Because small plastic scintillator is installed on the vacuum chamber directly, it has capability to have high sensitivity for localized spot area beam loss. On the other hand, the PMT can precisely be operated without being affected by magnetic field by keeping the PMT from the magnet. The new BLM leads the RCS to achieve the stable high power beam operation. In this presentation, we report the detail of the performance of the new BLM.
Hayashi, Naoki; Kato, Yuko; Miura, Akihiko; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*
Proceedings of 5th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2016) (Internet), p.368 - 371, 2017/03
It is important to understand why the beam loss occurs during user operation. It is understandable that the beam loss results from RF cavities failure. However, it would be still useful to study the beam loss detailed mechanism and to know which beam loss monitor (BLM) experiences the highest loss or is most sensitive. This may lead a reduction in the number of interlocked events and a more stable accelerator operation. The J-PARC Linac BLM has a simple data recorder that comprises multiple oscilloscopes. Although its functionality is limited, it can record events when an interlock is triggered. Of particular interest here are the events associated with only the BLM Machine Protection System (MPS). These may reveal hidden problems with the accelerator.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamamoto, Kazami
Proceedings of 5th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2016) (Internet), p.673 - 677, 2017/03
The most important issue in realizing such a MW-class high-power routine beam operation is to keep machine activations within a permissible level, that is, to preserve a better hands-on-maintenance environment. Thus, a large fraction of our effort has been concentrated on reducing and managing beam losses. To validate the beam loss optimizations, residual radiation measurement along the ring provide us with further information. By relating signals of the beam loss monitors with the measured distribution of the residual radiation, achievements of the high power beam operation will be described. In this presentation, we will report on the measurement results of residual radiation distribution along the ring together with the relation with the beam loss signals.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Okabe, Kota; Kamiya, Junichiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.314 - 318, 2016/11
The 3 GeV Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) project generates 1MW proton beam for the neutron experiments and Main ring accelerator. In case of such high intensity hadron accelerator, the most important issue is to reduce the uncontrolled loss. The beam collimation system is designed for this purpose. In the present design, the physical aperture is 1.5 times wider than the primary collimator aperture and the beam loss can be enough localized on this condition. After a startup of RCS in 2007, the collimator system of RCS worked well. But vacuum leakage occurred during the maintenance period in April, 2016. Since it was expected that the beam collimator was radio-activated very much, we took the influence of radiation into consideration and designed the collimator (ie. a remote clamp system to connect/take off it with a vacuum flange away from itself). Therefore, during the recovery work of the collimator, we were able to reduce the worker dose to less than 60 micro Sv though the collimator block had a residual dose of 40 mSv/h.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1097 - 1101, 2016/11
In the 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), a beam collimation system which aims to localize the beam loss at the collimators and to reduce the level of residual doses at the other devices is installed in the ring to achieve a 1MW high power beam operation. However vacuum leakage due to the collimator trouble occurred in April, 2016. Therefore an absorber No.5 in the collimation system had to be removed from the ring. Before resuming the beam operation, a new beam loss situation was simulated by using the particle tracking code. In the beam tuning, the transition of the beam loss distribution was measured by the beam loss monitors. We verified that the new beam situation was permissible, and the beam operation can be resumed. By following-up the transition of the residual dose distribution along the ring, the detailed beam loss structure can be understood. In this presentation, we report an influence of ring-collimator malfunction on beam loss localization in the J-PARC RCS.
Yamamoto, Kazami
Proceedings of 4th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2015) (Internet), p.80 - 84, 2016/02
The 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron of the J-PARC accelerates a proton beam up to 3 GeV and delivers it to the main ring and the material and life science facility. The main magnets (dipole and quadrupole magnets) of the synchrotron have large aperture, and thickness of yoke is larger than 200 mm. Considering the stopping power of a proton, a shielding effect of the magnets for beam loss monitor strongly depends on the lost beam energy. When the beam loss occurs during injection, the lost proton cannot penetrate the magnet yoke. But when the beam loss occurs after acceleration, lost beam easily pass the magnet. Therefore the signal response of the beam loss monitor is changed by the lost energy. We estimated the signal dependence on the lost energy by the simulation. The results indicated that the response strongly depends on the location of the lost point and lost energy. It is proportional to the lost power except the condition that the magnets become the radiation shielding.
Sakamoto, Shinichi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Konno, Chikara; Harada, Masahide; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Muto, Suguru*; Fujimori, Satoru*; Ono, Takehiro; Ikeda, Yujiro
JAERI-Tech 2001-075, 168 Pages, 2001/12
no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Masayoshi; Kinsho, Michikazu; Takeuchi, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 20th International Linac Conference, p.651 - 653, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Masayoshi
Proc. of 2nd Int. Topical Meeting on Nuclear Applications of Accelerator Technology (AccApp'98), p.566 - 571, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Noda, Fumiaki*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Kusano, Joichi; Mizumoto, Motoharu
Proc. of 11th Symp. on Accelerator Sci. and Technol., p.350 - 352, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Yoshiteru; Ishibori, Ikuo; Okumura, Susumu; Nara, Takayuki; Yokota, Wataru; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro; Agematsu, Takashi; Arakawa, Kazuo; Mizuhashi, Kiyoshi; Sano, M.*; et al.
JAERI-M 94-007, 74 Pages, 1994/02
no abstracts in English
Kato, Shinichi; Yamamoto, Kazami; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hotchi, Hideaki; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
The J-PARC 3-GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) accelerates proton beams from 400 MeV to 3 GeV and the designed output beam power is 1 MW. To achieve a high-intensity output beam power, the RCS adapts H charge-exchange multi-turn injection. The H
charge-exchange multi-turn injection. The H beam from the Linac is delivered to the RCS injection point, where it is injected through a carbon stripper foil in order to strip two electrons and to convert into proton. This injection is divided into 308 turns. Therefore, the both injection and circulating beams hit the foil repeatedly and scattering occur during the injection. Especially, large-scattered particles cause uncontrolled beam losses at downstream area. Thus, a new collimation system was developed and installed downstream of the foil to localize these losses in 2011. In the beam commissioning at 181 MeV and 400 MeV injection energy, unique tuning method of the collimator has been established and consequently these uncontrolled beam losses were localized successfully.
beam from the Linac is delivered to the RCS injection point, where it is injected through a carbon stripper foil in order to strip two electrons and to convert into proton. This injection is divided into 308 turns. Therefore, the both injection and circulating beams hit the foil repeatedly and scattering occur during the injection. Especially, large-scattered particles cause uncontrolled beam losses at downstream area. Thus, a new collimation system was developed and installed downstream of the foil to localize these losses in 2011. In the beam commissioning at 181 MeV and 400 MeV injection energy, unique tuning method of the collimator has been established and consequently these uncontrolled beam losses were localized successfully.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
Suppression of device radiations due to beam losses in the high intensity proton accelerators is one of the key issues to achieve MW class high power beam operation. In the J-PARC RCS, Ring collimator system which can localize the beam loss in the ring is adopted to suppress the device radiations. However, high residual doses are observed around the stripper foil. During the multi-turn charge exchange beam injection, not only the injecting beam but also circulating beam hit the foil, and then a large number of secondary particles, namely protons and neutrons, are generated. PHITS simulation results indicate that the secondary particles cause the high residual doses around the foil. Thus, we developed a new BLM which can detect the beam loss at the localized spot area. This new BLM can relate the beam loss with the radio activation of the device at the spot area. Detected radiations by this new BLM are occurred during the beam injection period and the total amount of the signal is directly proportional to the frequency of both the injecting and the circulating beam irradiation. Beam loss evaluation method combining the detailed residual dose survey by the GM counter after the beam stop into the radiations measurement by the BLM during the beam operation is effectively to reveal the beam losses structure from the point of view of the beam dynamics in the accelerator. In this presentation, we report the relation between the BLM signals and residual doses, and the beam losses structure and the mechanism.
Hayashi, Naoki
no journal, ,
In order to realize stable accelerator operation, it is necessary to understand various interlocked events and take countermeasures. In the J-PARC Linac, many interlocked events which include waveform data of current monitors and beam loss monitors, were recorded and classified to the various pattern. Their counter measures are under consideration. In the RCS (Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron), new processing unit is prepared to record beam current and position date of interlocked event and its future perspective will be reported.